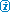
| Inkjet Printers - Summary Printers > Inkjet > Index | Navigation Icons Guide
|
| Origins - Invention by Carl Hellmuth Hertz, used in Mingograph. Developed by: |  |
Merits
| Problems
|
Inkjet Market - predominantly home printing and SOHO (Small Office / Home Office)
From 1990 onwards inkjets have been the first choice for home general printing.
Overview of the Inkjet Print Process
A non-contact printhead with small nozzles. Thermal or piezoelectric ejection of liquid ink droplets from the nozzles in picolitre quantities making pixels of liquid ink at between 300 and 5,000 dpi. The higher resolutions are not normally discernible with the naked eye but give sub-pixel cells for colour dithering.
History & Overview.
Early history - Mingograph and Siemens. Dr Sweet and continuous inkjet. 
Drop on demand thermal inkjet pioneered by a team led by Frank Cloutier at HP starting in 1979 and delivering the "Thinkjet" in 1984.  The "Deskjet" had laser like 300dpi print but cost less to buy.
The "Deskjet" had laser like 300dpi print but cost less to buy. 
Epson developed the piezoelectric inkjet.
Market - right product / right time, graphical printing just as MS - Windows became popular. 
Fairly simple carriage scanning mechanism using light duty motors similar to a dot-matrix.
Mass production aimed at home-user photography potentially changes other markets too.
Technology - two classes of product.
Continuous Ink - an industrial production line technology that won't scale down. 
Drop on Demand - printheads are a row of hundreds of jets individually addressed by the printers internal computer. 
Printheads can be:
Thermal - printheads are easy to make but aren't always robust. 
Piezoelectric - much more robust but difficult to make an effective head at low cost. 
Ink - an old idea but inkjet material is a new version - problems of kogation and fading. 
Application - ink can be applied by several methods, plate, impact - inkjet heads unusual. 
![]()
Inkjets In Practice - tend to aim at a market segment:
Low price - usually colour but slow. 
Home photography - more cartridges, often have a preview screen and pictrbridge. 
Wide format - A3 up to A0. 
Office workgroup - usually have two trays, may have duplex and a wired network. 
Digifeiting - printers work so well a problem is emerging with counterfeiting. 
Costs in theory - the inkjet mechanism involves special inks and complex heads. Theoretically mass production of heads, inks and other components could make inkjet printing quite cheap. 
Current Inkjets and costs in practice. Cheap to buy, expensive to run. 
--
Ink - in an inkjet is primarily liquid carrier - propellant with some colourant -dye or pigment. 
Ink problems and possibilities. Scientific development of ink is comparatively recent. All sorts of possibilities in print - books, newspapers and even wallpaper. Using air or UV curing polymers inkjets can be used for micromanufacturing. 
Ink History - soot and oil, ferrous sulphate and oak gall. Ink formulation bound up with the application method. Relationship between inks, dyes and paints. 
Application method and ink - brushes, pens and printing presses. 
Scientific Colours - Dye chemistry and Parker Quink the first scientific ink. 
Modern Inks - relationship between laser, thermal, impact and liquid inks. 
Colourant -light is electromagnetic radiation and tends to give information about the materials which orignated or reflected it.  Paints and printing are ways of misleading the eye using:
Paints and printing are ways of misleading the eye using:
Dyes - molecular scale dissolved material forming very small crystals on paper fibers. 
Pigments - mechanically ground or emulsified plates of material. 
Colours - Additive RGB and subtractive CMY process. What are the chemicals? 
Liquid Carrier -
Water, Alcohol - Mixes and add glycol. 
Inkjet Ink - original aim was just to use ordinary ink.
Problems - Ink as propellant. Air locks, viscosity, Kogation, Chemical Attack, Colour stability.
so ordinary ink isn't ideal. 
Merits - delivered in a small tank carefully designed. Usually supplied in small quantities. Printer can use things like halogen or UV lights to fix ink. 
--
Printheads. 
Principles:
Continuous - pressure fed droplets steered electrostatically- impractical on a small scale. 
![]()
Drop on Demand - capillary ejects a drop on a thermal or piezoelectric stimulus. 
Thermal - used by most consumer printers. Heaters in the walls of capillary tubes. 
Heaters - thin film resistors on a glass, ceramic or silicon substrate. 
Thermal Cycling - room temperature to 300C tens of thousands of times per second. 
Ink Chemistry - avoid kogation and attacks on components. 
Head Types
Roof-Shooter - heater under the orifice, ink drive directly and symetrically at it. 
Edge-Shooter - heaters in one wall of the channels. Ink driven sideways. 
Manufacturers - Canon, HP, and Lexmark make thermal heads on a large scale. 
Refills - Cartridge matched to head life. Not repairable, may be refillable. 
Piezoelectric - PZT crystal changes shape and drives ink through a chamber. 
Epson makes consumer-oriented printers. Main problem to avoid air bubbles. 
Xerox Phasers - solid ink molten at 135C. 
Industrial Inkjet Heads - usually stainless steel multi-jet assemblies. 
Piezoelectric limits - can have thousands of elements. 
Other Mechanisms - Samsung electromagnetic ball-bearing mechanism. 
--
Head Design Compromises - print quality, speed, reliability,manufacturing technology and ease of use. More nozzles and faster performance can raise print speeds or lift printout quality. 
Swath
Pagewidth Swath - practical in industrial machines but not (yet) in consumer devices. 
Shuttle
Slightly fewer than pagewidth elements - used in the phaser. 
Speed & Resolution - Multiple head elements can raise quality, speed or both. 
Firing Rate - bubble 10us but refill 80 to 200 us. 
Print Elements - HP Thinkjet 12 elements - now hundreds per head. 
Electrical Mechanism - Simple cartridges connector per head element. 
Integrated Drivers - Build an IC SERDES into the head to handle data - and use-by dates. 
Pagecounts and Use By Dates - and chip resetters. 
Printhead Life.
Drying Out - should be parked on the service station. 
Wear - only real contact is with the service station. 
Reliability Issues - Disposable heads, Seperate heads, Piezoelectric heads. 
Basis of the printer is a raster scanning design, carriage and paper feed.
Printheads:
Thermal printheads. 
Piezoelectric printheads. 
Cartridges
The CMYK Process. 
Single Cartridge - one cartridge - tricolour, four colour, swappable. 
Two Cartridges - one tricolour and one black. 
Four Cartridges - one each for CMY and possibly a large Black. 
Seven Cartridges - lighter tones for CMY, then normal CMYK. 
Eight Cartridges - Cyan, Magenta, Yellow, Red, Blue, Black, Mat Black, Gloss. 
Cartridges & Pagecover - Cartridges often don't have much ink - 10 millilitres used in 1 to 10 picolitre drops giving about 7 full-cover pages to one cartridge or 28 for CMYK. 
Ink Delivery - the amount of ink that can be shipped affects the value. 
Cartridge on Carriage - heavy carriage with several millilitres of ink slopping around. 
Cartridge in Base - lighter carriage but problematic plumbing. 
Service Station - protects and purges the head. 
Paper Transport & Carriage Action. 
Printers generally designed for cut-sheet, but often with limited capacity trays
Duplex - built in on some SOHO models. 
Platen Gap - not normally adjustable. 
Linefeed Motors - steppers, usually with planet wheels to work the paper feed. 
Carriage Drive
Stepper -cheap. 
DC - servo - usually faster and gives the accuracy required. 
Single Motor designs - possible using various mechanical linkages.
Interface - Usually USB. USB and even WiFi becomming more common. 
Minimal Manufacture - inkjet construction aims to deliver maximum function at minimum price. 
Micromanufacturing - inkjets can be used to label cables and bottle. Creating electronic assemblies using inkjet printed polymers. 
Foodstuffs
Micromanufactured Objects
3D printing -
--© Graham Huskinson 2010
This page is like all those in the "book" section in being under development.
If you think this page is wrong in some respect or have better information on how things are done let us know. Click here.